-
- News Center
- Related News
-
- Round Edge Aluminum Strip For Transformer Winding
Round edge aluminum strip for transformer winding is made from high-purity aluminum (such as 1060-O alloy) through rolling, annealing and other processes. The aluminum strip features rounded corners or edges, resulting in high conductivity, a smooth, burr-free surface, and high dimensional accuracy. This aluminum strip is specifically designed for use in the manufacture of high and low voltage transformer windings.
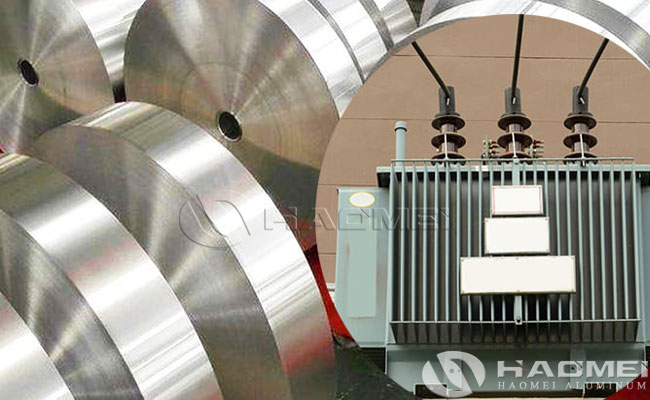
Material and Processing
Material:
Primarily 1060-O alloy pure aluminum, with an aluminum content of ≥99.6%, meeting the GB/T 3190-1996 standard. Its conductivity is second only to copper, but at a lower cost, making it an ideal alternative material for transformer windings.
Processing:
Produced through rolling, annealing, and other processes, the aluminum strip achieves a smooth, scratch-free surface. The edges are chamfered (rounded corners or edges) to eliminate burrs and prevent damage to the insulation layer during winding.
Physical Properties
Thickness and Width:
Thickness ranges from 0.2mm to 3.0mm, and widths from 20mm to 1650mm. Custom aluminum strip for transformer can be made to meet the needs of varying specifications.
Resistivity: ≤0.028Ω·mm²/m, ensuring winding conductivity and reducing energy loss.
Mechanical Properties: Complies with TUN900 069-1998 standard. In the annealed state (O state), it is soft, easy to wind, and resistant to breakage.
Packaging
Packaged on wooden pallets with an inner diameter of 300mm or 500mm to prevent deformation during transportation.
Aluminum strip with round edges is a conductive material created by rounding the edges of rectangular pure aluminum or alloy aluminumstrip using specialized equipment. Its primary application is winding high-voltage or low-voltage windings in transformers, providing current conduction. The essence of round edges is to address the "corner defects" of rectangular aluminum strip. The specific reasons can be summarized into five points:
- Preventing insulation damage:
The sharp corners of rectangular aluminum strip can pierce the insulating paper/varnish wrapped around the winding during winding and operation, causing damage to the insulation layer.
- Reducing local electric field concentration:
When a transformer is operating, sharp corners generate extremely strong local electric fields (the "tip discharge effect"), far exceeding the insulation material's tolerance limit and easily causing insulation breakdown.
- Improving winding processability:
Rounded edges reduce "stuck" and "stress concentration" during winding, preventing cracks in the aluminum strip caused by the stress of the corners, while also protecting operators' hands from scratches.
- Improving electrical conductivity:
The smooth surface of round edge aluminum strip improves electrical conductivity and reduces resistance losses.
- Reducing noise:
The use of round edge aluminum strip can reduce transformer noise during operation and improve overall equipment performance.
Applications of round edge aluminum strip for transformer:
- Dry-Type Transformer Windings
As a conductive material for high and low voltage windings, replacing copper windings significantly reduces equipment size and weight (aluminum's density is only one-third of copper's) while improving insulation performance.
Flame-retardant, pollution-free, and with minimal partial discharge, it is suitable for safety-critical applications such as high-rise buildings, underground facilities, and commercial centers.
- Large Transformers and the Power Industry
In large transformers, the rounded edge design reduces winding stress and improves winding stability.
It is moisture-resistant, operates smoothly, and is quiet, reducing maintenance costs by approximately 30% compared to copper windings.
- Solar Energy and New Energy
Used in photovoltaic inverter transformer windings, it withstands harsh outdoor environments and extends equipment life.
Due to its low cost and stable performance, round edge aluminum strip has been adopted for transformer winding manufacturing in many countries, including the United States (where it is widely used in distribution transformers), India (where aluminum production capacity is significant and demand is growing), some European countries (adopted as part of the distribution transformer transition), and Italy (which was an early adopter of aluminum-wound transformers).
- Haomei aluminum
- haomei Aluminium Plate





